
table of contents
Urinary excretion heavy metal test
Urinary excretion heavy metal test results in August 2016
Excerpt from record 12
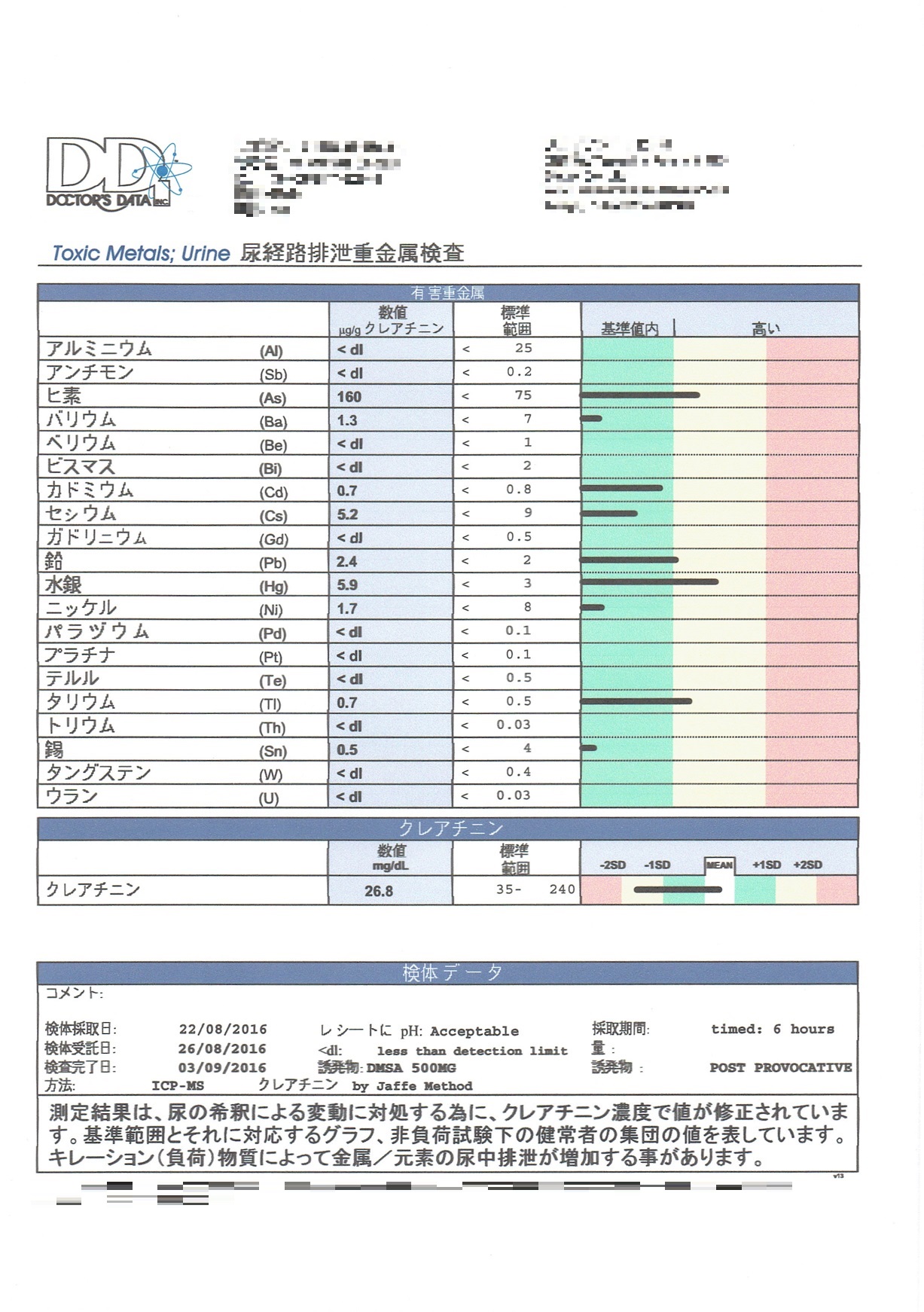
Urinary excretion heavy metal test
Harmful heavy metal
Numerical value,Standard range,Within standard value,high
Aluminum
Antimony
Arsenic
Barium
Beryllium
Bismuth
Cadmium
Cesium
Gadolinium
Lead
Mercury
Nickel
Palladium
Platinum
Tellurium
Thallium
Thorium
Tin
Tungsten
Uranium
Creatinine
Creatinine
Sample data
The determination result is corrected by the creatinine concentration, taking into consideration the fluctuation due to urine dilution.
It shows the reference range and the corresponding graph, and the value of the population of healthy subjects under the unloaded test.
Chelation substances may increase urinary excretion of metals/elements.
Comparison of test results
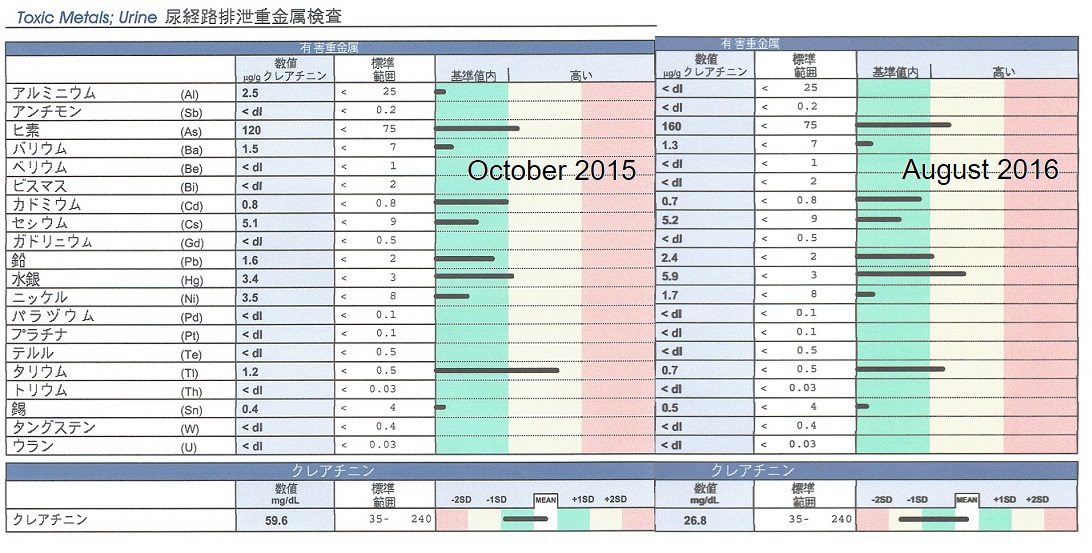
The comparative data is from October 2015 and August 2016.
The data on October 2015 is on the left, and the data on August 2016 is on the right.
Urinary excretion Heavy metal test 20 items compared.
Aluminum 2 5 → <dl Go down
Antimony <dl → <dl No detection
Arsenic 120 → 160 Go up
Barium 1 5 → 1 3 Go down
Beryllium <dl → <dl No detection
Bismuth <dl → <dl No detection
Cadmium 0 8 → 0 7 Go down
Cesium 5 1 → 5 2 Go up
Gadolinium <dl → <dl No detection
Lead 1 6 → 2 4 Go up
Mercury 3 4 → 5 9 Go up
Nickel 3 5 → 1 7 Go down
Palladium <dl → <dl No detection
Platinum <dl → <dl No detection
Tellurium <dl → <dl No detection
Thallium 1 2 → 0 7 Go down
Thorium <dl → <dl No detection
Tin 0 4 → 0 5 Go up
Tungsten <dl → <dl No detection
Uranium <dl → <dl No detection
High values of arsenic, lead, mercury and thallium are not excreted in abnormal amounts.
Still, since it exceeds the standard value, a large amount of heavy metals are accumulated.